
- #LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT HOW TO#
- #LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT INSTALL#
- #LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT UPDATE#
- #LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT SOFTWARE#
- #LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT WINDOWS#
#LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT INSTALL#
Run the following command to install TightVNC on RHEL-based distributions: $ sudo yum -y install tigervnc-server xorg-x11-fonts-Type1
#LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT SOFTWARE#
This software allows remote desktop management and control. Step 2: Installing the TightVNC serverĪfter you have installed the desktop environment, it is time to install the TightVNC software. The choice of display manager in this tutorial does not affect the connection to the VNC server because you will be using XFCE or GNOME to connect to the VNC client, XFCE or any GUI has already logged you in as a non-root user, therefore, select the display manager that suits your needs and press Enter, and choosing it will not make any changes in this tutorial. Display Manager is a tool that provides a graphical user interface for selecting and entering the desktop environment. Note that when installing Xfce you will be prompted to set the default display manager. Therefore, to install XFCE on Debian-based distributions, enter the following command so that by installing the xfce4-goodies packages, your desktop environment will have more advanced features: $ sudo apt install xfce4 xfce4-goodies The XFCE GUI, which provides a fast and stable connection together with the TightVNC software, is more compatible with Debian-based distributions. Then run the following command to install the GNOME desktop environment, which is more compatible with RHEL-based distributions: $ sudo dnf groupinstall "Server with GUI"
#LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT UPDATE#
If you have installed a minimal version of the operating system, which by default only provides a command line interface and no GUI, The first step to installing VNC should be to install the GNOME or XFCE GUI or other graphical options so that you can easily interact with the remote VNC server.įirst, connect to your server through an SSH tunnel and update your Linux system packages: sudo apt update Step 1: Installing the desktop environment Note: There are many VNC client programs in Linux that you can choose from vinagre, krdc, RealVNC, or TightVNC according to your needs and compatibility with your system.
#LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT HOW TO#
Therefore, in this article, we have decided to teach how to install and set up VNC in Linux distributions based on Debian and RHEL distributions through the most advanced version of VNC software (TightVNC) so that you can connect to the VNC server through the SSH tunnel and Interact with the VNC server using the graphical desktop environment and VNC client program on your local system. In this situation, you can connect to the computer on which the VNC server component is configured and manage the remote computer through a Duplicate screen that is presented to users by the server from the remote computer. To benefit from the features of this software, you need to install and run the VNC server on the Linux system, and you also need a VNC viewer and a secure TCP/IP connection to interact with the VNC server.
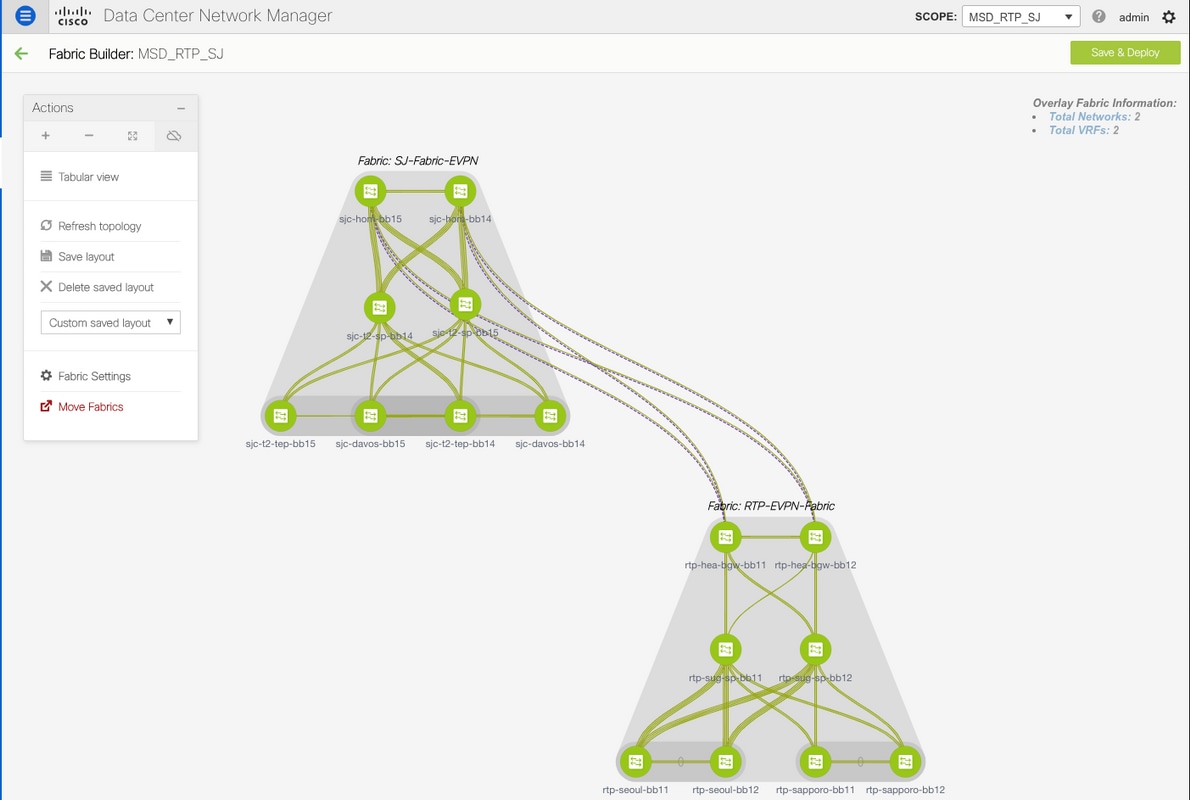
This software has been able to facilitate the tasks of Linux administrators without the need for physical presence and they can access the Linux server desktop remotely through VNC. VNC even offers the ability to use keyboard and mouse clicks to communicate with the server and apply settings. This control system can manage files and software on computers connected to the Internet, and Users can even remotely intervene in their server settings via VNC using the Linux command line.
#LINUX DEPLOY VNC CONNECT WINDOWS#
The VNC software also supports the Windows operating system, and communication with the Linux server through this software has become much more efficient and simple for Windows users. VNC, which stands for Virtual Networking Computing, is a remote connection system and sharing system that, with its emergence in the 1990s, provided remote access to the desktop graphical environment on a server for Linux systems similar to MSTSC on Windows.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
